The field of genomics experiences a seismic transformation with the advent of next-generation sequencing (NGS). Among the leading players in this landscape, HK1 stands out as its powerful platform facilitates researchers to explore the complexities of the genome with unprecedented accuracy. From deciphering genetic differences to pinpointing novel drug candidates, HK1 is transforming the future of healthcare.
- The capabilities of HK1
- its impressive
- sequencing throughput
Exploring the Potential of HK1 in Genomics Research
HK1, the crucial enzyme involved in carbohydrate metabolism, is emerging being a key player throughout genomics research. Scientists are initiating to reveal the intricate role HK1 plays with various cellular processes, opening exciting opportunities for illness diagnosis and drug development. The capacity to control HK1 activity might hold tremendous promise for advancing our insight of challenging genetic disorders.
Moreover, HK1's quantity has been linked with different clinical outcomes, suggesting its capability as a prognostic biomarker. Coming research will definitely reveal more understanding on the multifaceted role of HK1 in genomics, pushing advancements in customized medicine and biotechnology.
Exploring the Mysteries of HK1: A Bioinformatic Analysis
Hong Kong protein 1 (HK1) remains a puzzle in the realm of biological science. Its intricate purpose is still unclear, impeding a thorough understanding of its impact on organismal processes. To decrypt this biomedical challenge, a comprehensive bioinformatic exploration has been conducted. Leveraging advanced techniques, researchers are aiming to reveal the latent mechanisms of HK1. hk1
- Preliminary| results suggest that HK1 may play a crucial role in cellular processes such as growth.
- Further analysis is necessary to corroborate these findings and elucidate the exact function of HK1.
HK1 Diagnostics: A Revolutionary Path to Disease Identification
Recent advancements in the field of medicine have ushered in a new era of disease detection, with focus shifting towards early and accurate characterization. Among these breakthroughs, HK1-based diagnostics has emerged as a promising approach for pinpointing a wide range of illnesses. HK1, a unique protein, exhibits distinct properties that allow for its utilization in sensitive diagnostic tests.
This innovative approach leverages the ability of HK1 to interact with disease-associated biomarkers. By analyzing changes in HK1 activity, researchers can gain valuable insights into the absence of a medical condition. The promise of HK1-based diagnostics extends to variousmedical fields, offering hope for more timely management.
The Role of HK1 in Cellular Metabolism and Regulation
Hexokinase 1 catalyzes the crucial first step in glucose metabolism, converting glucose to glucose-6-phosphate. This transformation is critical for tissue energy production and regulates glycolysis. HK1's function is stringently governed by various pathways, including conformational changes and methylation. Furthermore, HK1's organizational localization can influence its role in different areas of the cell.
- Impairment of HK1 activity has been linked with a spectrum of diseases, including cancer, diabetes, and neurodegenerative conditions.
- Deciphering the complex relationships between HK1 and other metabolic processes is crucial for developing effective therapeutic interventions for these diseases.
Harnessing HK1 for Therapeutic Applications
Hexokinase 1 HXK1 plays a crucial role in cellular energy metabolism by catalyzing the initial step of glucose phosphorylation. This molecule has emerged as a potential therapeutic target in various diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. Targeting HK1 activity could offer novel strategies for disease treatment. For instance, inhibiting HK1 has been shown to reduce tumor growth in preclinical studies by disrupting glucose metabolism in cancer cells. Additionally, modulating HK1 activity may hold promise for treating neurodegenerative diseases by protecting neurons from oxidative stress and apoptosis. Further research is needed to fully elucidate the therapeutic potential of HK1 and develop effective strategies for its manipulation.
 Rider Strong Then & Now!
Rider Strong Then & Now! Brian Bonsall Then & Now!
Brian Bonsall Then & Now!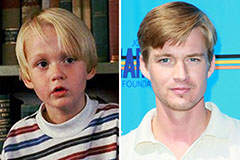 Mason Gamble Then & Now!
Mason Gamble Then & Now! Karyn Parsons Then & Now!
Karyn Parsons Then & Now! Kane Then & Now!
Kane Then & Now!